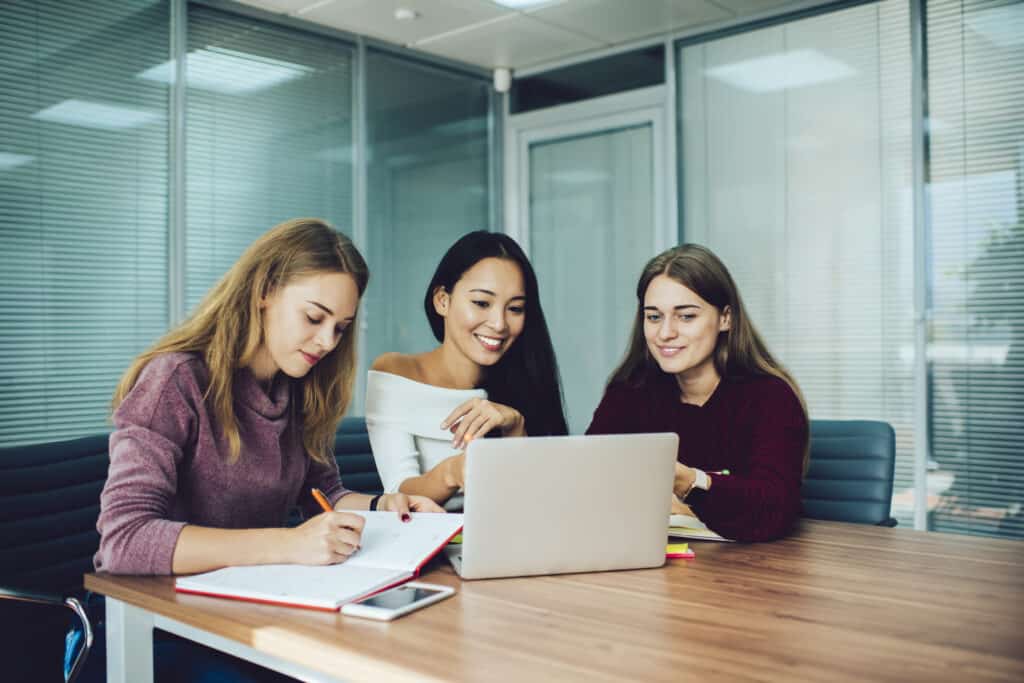
Navigating the complex landscape of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) requires a multifaceted approach, and therapy stands as a cornerstone in its treatment. ASD, a developmental condition characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors, manifests uniquely in each individual, necessitating personalized therapeutic interventions. In this blog, we delve into the pivotal role of therapy in addressing the diverse needs of individuals across the autism spectrum. Therapeutic interventions encompass a spectrum themselves, ranging from behavioral therapies to speech and language therapy, occupational therapy, and beyond. Each modality aims to enhance the individual’s quality of life, mitigate challenges, and unlock their potential for growth and development. With early intervention and tailored therapeutic strategies, individuals with ASD can cultivate essential skills, improve their independence, and thrive within their communities. Join us as we explore the transformative impact of therapy in empowering individuals with ASD to lead fulfilling lives.
Navigating Social Interactions: The Role of Social Skills Therapy in Autism

Social interaction is a fundamental aspect of human experience, facilitating connections, understanding, and collaboration. However, for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), navigating social situations can present unique challenges. Social skills therapy offers a tailored approach to address these difficulties, equipping individuals with the tools and strategies necessary to navigate social nuances effectively. In this article, we delve into the significance of social skills therapy in supporting individuals with ASD, exploring its methodologies, benefits, and impact on fostering meaningful social connections.
Key Components of Social Skills Therapy
Social skills therapy encompasses a range of strategies tailored to the unique needs of individuals with ASD. These may include role-playing exercises, social stories, video modeling, and group activities aimed at practicing and reinforcing social skills in real-life scenarios. Therapists work closely with individuals to identify specific areas of difficulty and develop personalized goals and strategies for improvement.
Building Empathy and Perspective-Taking
Empathy and perspective-taking are essential components of successful social interaction. However, individuals with ASD may struggle to understand the thoughts, feelings, and intentions of others. Social skills therapy includes exercises and activities focused on developing empathy, such as perspective-taking games, role reversals, and discussions about emotions, helping individuals recognize and respond appropriately to the feelings of others.
Enhancing Communication Skills
Effective communication is vital for navigating social interactions. Social skills therapy targets communication deficits commonly associated with ASD, such as difficulties with initiating and maintaining conversations, understanding nonverbal cues, and interpreting sarcasm or humor. Through targeted interventions, individuals learn communication strategies, such as active listening, turn-taking, and expressing thoughts and feelings clearly and appropriately.
Practicing Social Scenarios
Practice is crucial for mastering social skills and building confidence in social settings. Social skills therapy provides opportunities for individuals to practice newly acquired skills in structured, supportive environments. Role-playing exercises, group discussions, and real-life simulations allow individuals to apply learned skills, receive feedback, and refine their social interactions in a safe and controlled setting.
Promoting Peer Interaction and Peer Relationships
Peer interaction plays a significant role in social development and integration. Social skills therapy often incorporates group sessions where individuals with ASD can interact with peers in a supportive and structured environment. These group settings provide opportunities for practicing social skills, forming friendships, and developing a sense of belonging within a peer group.
Harnessing Strengths: A Holistic Approach to Therapy for Autism
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) presents unique challenges, but individuals also possess remarkable strengths and talents. A holistic approach to therapy acknowledges and leverages these strengths to promote growth and well-being. In this article, we explore the importance of embracing strengths in therapy for autism.
- Strength-Based Intervention: Rather than solely focusing on deficits, therapy for autism should identify and build upon individual strengths. This approach fosters confidence, resilience, and a sense of empowerment.
- Individualized Support: Tailoring interventions to capitalize on strengths ensures a personalized approach that resonates with each individual’s abilities, interests, and goals.
- Promoting Self-Esteem: Recognizing and nurturing strengths enhances self-esteem and self-efficacy, empowering individuals to face challenges with optimism and determination.
- Encouraging Independence: By harnessing strengths, therapy cultivates skills that promote independence and self-reliance, fostering greater autonomy and life satisfaction.
Beyond Behavior: A Comprehensive Look at Behavioral Therapy for Autism
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is characterized by a wide range of behaviors that can present significant challenges for individuals and their families. Behavioral therapy, a cornerstone in the treatment of ASD, goes beyond merely addressing observable behaviors; it delves into understanding the underlying causes and motivations behind these behaviors. In this article, we take a comprehensive look at behavioral therapy for autism, exploring its principles, methodologies, and transformative impact on individuals with ASD and their families.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is one of the most widely recognized and empirically supported forms of behavioral therapy for autism. ABA involves breaking down complex behaviors into smaller, manageable components and using systematic interventions to teach and reinforce desired behaviors while reducing challenging ones. Through techniques such as reinforcement, prompting, and shaping, individuals with ASD learn new skills and behaviors in a structured and supportive environment.
Individualized Treatment Plans
One of the strengths of behavioral therapy is its emphasis on individualized treatment plans tailored to the unique needs and abilities of each individual with ASD. Therapists conduct thorough assessments to identify specific areas of difficulty and develop personalized goals and strategies for intervention. This person-centered approach ensures that interventions are targeted, effective, and meaningful for the individual and their family.
Addressing Challenging Behaviors
Challenging behaviors, such as aggression, self-injury, or repetitive behaviors, are common among individuals with ASD and can significantly impact their quality of life. Behavioral therapy focuses on understanding the function of these behaviors and implementing strategies to address underlying causes while teaching alternative, more adaptive behaviors. By replacing challenging behaviors with more appropriate ones, individuals can enhance their social functioning, communication, and overall well-being.
Building Functional Skills
In addition to addressing challenging behaviors, behavioral therapy aims to teach individuals with ASD a wide range of functional skills necessary for daily living. These may include self-care skills, communication skills, social skills, and academic skills, among others. By breaking down these skills into manageable steps and providing systematic instruction and reinforcement, individuals can develop greater independence and competence in various areas of life.
Family Involvement and Collaboration
Family involvement is integral to the success of behavioral therapy for autism. Therapists work closely with families to develop and implement intervention plans, provide training and support, and monitor progress over time. By involving families in the therapeutic process, behavioral therapy extends beyond the therapy sessions and into the home environment, where skills can be reinforced and generalized more effectively.
Conclusion
Therapy plays a crucial role in treating Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). With the right approach, individuals with ASD can learn to communicate, socialize, and thrive in their daily lives. At Positive Solutions Behavior Group LLC, our team of experienced therapists is dedicated to providing personalized support and guidance to help individuals with ASD achieve their full potential. By working together, we can create a brighter future for those affected by this complex and often misunderstood condition.
If you or someone you know is living with Autism Spectrum Disorder, we invite you to reach out to us at Positive Solutions Behavior Group LLC in Florence, Kentucky. Our friendly and knowledgeable staff is here to answer your questions and provide information on our therapy services. Contact us today at 859-282-0400 to take the first step towards a brighter future.