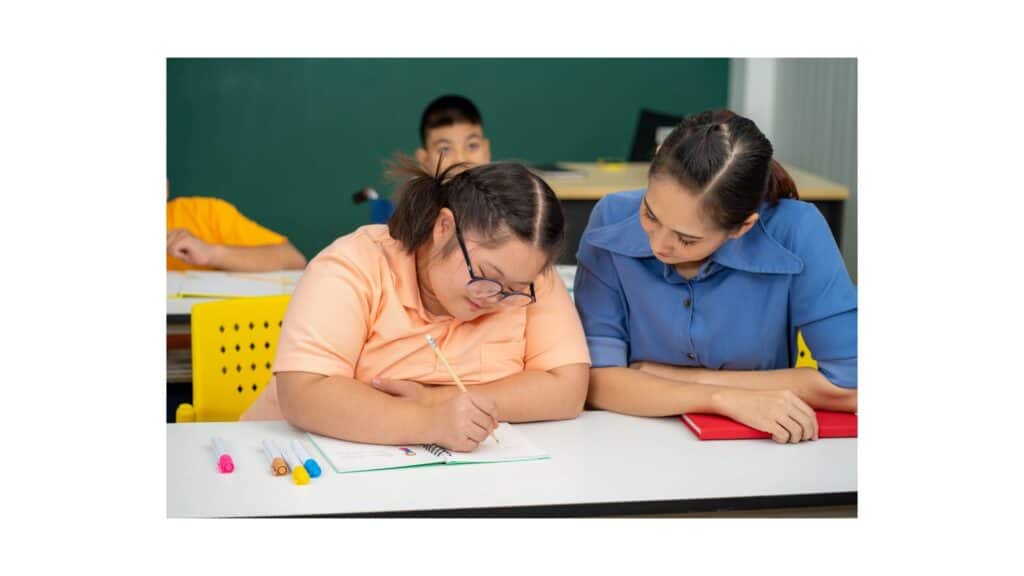
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is an effective approach for managing daily behavioral goals in children with developmental delays. This evidence-based practice focuses on understanding and modifying behaviors through positive reinforcement and structured interventions. By setting specific, measurable goals tailored to each child’s unique needs, therapists can promote skill development and enhance overall functioning. Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in this process, collaborating with therapists to reinforce desired behaviors in everyday situations. Consistent implementation of ABA techniques can lead to significant improvements in social skills, communication, and daily living activities.
Understanding ABA Therapy Principles
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is grounded in several core principles, including reinforcement, behavior modification, and data collection. By analyzing a child’s behavior, therapists identify the antecedents that trigger certain actions and the consequences that reinforce them. This comprehensive understanding allows for targeted interventions tailored to the individual child’s needs. Techniques such as positive reinforcement encourage desired behaviors while reducing unwanted ones. Through consistent application of these principles, ABA therapy aims to foster meaningful behavioral changes that improve a child’s ability to navigate daily life successfully.

The Principle of Reinforcement
Reinforcement is a fundamental principle in ABA therapy that encourages the repetition of desired behaviors. Positive reinforcement, such as verbal praise or tangible rewards, increases the likelihood that a child will engage in specific actions again. By recognizing and rewarding appropriate behavior, therapists create a motivational environment that fosters learning and growth, enabling children to develop essential skills and improve their overall behavior in various settings.
Understanding Behavior Modification
Behavior modification involves changing specific behaviors through systematic interventions. In ABA therapy, this process includes identifying unwanted behaviors and implementing strategies to decrease or replace them with more appropriate alternatives. Techniques such as prompting, shaping, and fading help modify behaviors gradually. By applying consistent behavior modification techniques, therapists can help children develop healthier habits and coping strategies, ultimately enhancing their ability to function successfully in everyday situations.
The Role of Data Collection
Data collection is essential in ABA therapy, providing objective evidence of a child’s progress and the effectiveness of interventions. Therapists track various behaviors through methods such as frequency counts or duration recording, allowing for data-driven decision-making. This ongoing assessment enables therapists to adjust strategies as needed and tailor interventions to meet the child’s evolving needs. Regular data analysis ensures that therapeutic goals remain relevant and achievable, promoting continuous improvement in the child’s behavior.
Tailoring Interventions to Individual Needs
ABA therapy emphasizes the importance of individualized interventions to address each child’s unique needs and challenges. By conducting thorough assessments, therapists gain insight into a child’s strengths, preferences, and areas requiring support. This information guides the development of customized goals and strategies, ensuring that interventions are relevant and effective. Tailored approaches empower children to build on their skills and achieve meaningful behavioral changes, fostering a greater sense of independence and self-efficacy.
Promoting Functional Skills for Daily Life
A primary focus of ABA therapy is promoting functional skills that enhance a child’s ability to navigate daily life. This includes teaching essential skills such as communication, social interactions, and self-care tasks. Therapists utilize various techniques, including modeling and role-playing, to ensure that children can generalize these skills across different environments. By focusing on functional skills, ABA therapy prepares children for greater independence, ultimately improving their overall quality of life and social integration.
Setting Achievable Behavioral Goals
Establishing clear, achievable behavioral goals is crucial in ABA therapy for children with developmental delays. These goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, a goal might involve a child using polite language during interactions or following instructions without prompts. By breaking down larger objectives into smaller, manageable tasks, therapists can create a structured environment that promotes success. Regular assessments ensure that these goals remain aligned with the child’s progress and evolving needs, making adjustments as necessary to foster continued development and learning.
The Role of Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement is a cornerstone of ABA therapy, serving as a powerful tool to encourage desirable behaviors in children. By providing rewards, such as praise, tokens, or tangible items, therapists can motivate children to engage in specific actions consistently. This approach not only increases the likelihood of repeating desired behaviors but also helps build self-esteem and confidence. Understanding the individual preferences of each child allows therapists to tailor reinforcement strategies effectively, ensuring that motivation remains high. Over time, this can lead to more significant behavioral changes and improved overall functioning.
Involving Parents in the Process
The involvement of parents and caregivers in ABA therapy is essential for achieving long-term success in managing daily behavioral goals. Parents can reinforce learned skills and behaviors at home, creating a consistent environment that mirrors therapeutic sessions. Collaborating with therapists enables parents to understand the techniques used and apply them effectively in everyday situations. Regular communication between therapists and families fosters a supportive network, ensuring that strategies are implemented consistently across different settings. This partnership not only enhances the child’s learning experience but also empowers parents to take an active role in their child’s development.
Tracking Progress and Adjustments
Monitoring progress is vital in ABA therapy, as it allows therapists to assess the effectiveness of interventions and make necessary adjustments. Data collection methods, such as frequency counts or interval recording, help track specific behaviors over time, providing insight into trends and patterns. This objective data enables therapists to identify which strategies are working and which may require modification. Regular review meetings with parents and caregivers ensure everyone is informed of the child’s progress, fostering a collaborative approach to refining goals and techniques. This ongoing evaluation is key to promoting continuous growth and development.
Social Skills Development through ABA
ABA therapy is instrumental in enhancing social skills among children with developmental delays. Through structured social interactions and targeted interventions, therapists can teach essential skills such as turn-taking, eye contact, and appropriate conversation starters. Role-playing and modeling behaviors in safe environments allow children to practice and refine their social skills. Moreover, therapists can create social scenarios that mimic real-life situations, helping children generalize these skills across different contexts. Improving social competence not only boosts a child’s confidence but also fosters meaningful relationships with peers, enhancing their overall quality of life.
Integrating Daily Living Skills
Integrating daily living skills into ABA therapy is crucial for promoting independence in children with developmental delays. Skills such as grooming, dressing, and meal preparation can be systematically taught using ABA techniques. Therapists can break down these tasks into smaller, manageable steps, using prompts and reinforcement to encourage successful completion. By practicing these skills in structured sessions and everyday situations, children can develop the confidence and competence needed for daily self-care. This focus on functional skills empowers children to navigate their environment more independently, significantly enhancing their overall quality of life.
The Importance of Consistency
Consistency is a fundamental aspect of successful ABA therapy for managing behavioral goals. Maintaining a structured routine helps children understand expectations and reinforces learning. Consistent application of behavioral interventions by both therapists and parents creates a predictable environment that fosters skill acquisition. Additionally, clear communication regarding rules and expectations across all settings—home, school, and therapy—ensures that children receive the same messages consistently. This cohesive approach minimizes confusion and maximizes the effectiveness of ABA strategies, ultimately leading to more significant behavioral improvements and better overall outcomes for the child.
Conclusion
ABA therapy is an invaluable tool for managing daily behavioral goals in children. At Positive Solutions Behavior Group LLC in Lakewood Ranch, FL, we strive to empower families with effective strategies that promote positive behaviors and enhance overall well-being. Our dedicated team works closely with each child to create personalized plans that address their unique needs, fostering growth and development in a supportive environment.
If you’re looking for effective behavioral strategies for your child, contact us at 859-282-0400. Together, we can build a brighter future and help your child thrive in their everyday life.