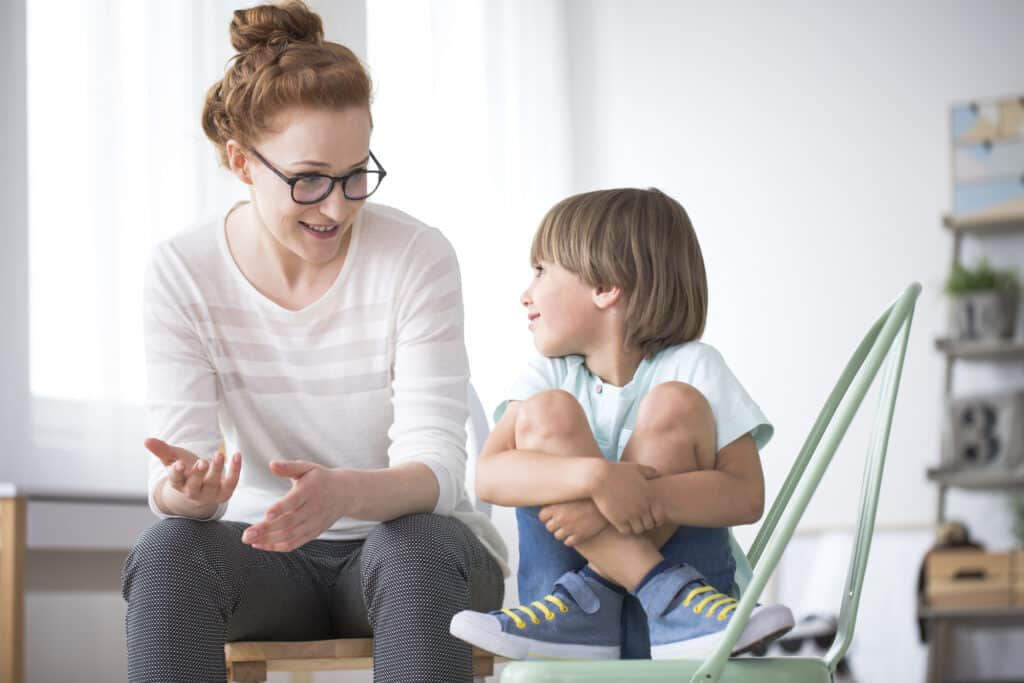
Understanding Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is pivotal in comprehending the intricacies of enhancing social interactions, particularly for individuals with neurodevelopmental disorders. As a multifaceted approach rooted in behavioral psychology, ABA therapy employs systematic strategies to modify behaviors and foster positive changes in various settings. This blog aims to demystify the core principles of ABA therapy, shedding light on its effectiveness in promoting social skills. By delving into its methodologies, techniques, and real-life applications, we unravel the nuanced ways ABA therapy can empower individuals to navigate social interactions more adeptly. Through insightful exploration and practical insights, readers can gain a deeper understanding of how ABA therapy serves as a catalyst for social growth and development.
The Foundations of ABA Therapy
At the core of ABA therapy lies a rich tapestry of principles and theories meticulously crafted to elevate social interactions. Grounded in the behavioral sciences, ABA therapy draws upon theories of learning, reinforcement, and motivation to shape behavior positively. By dissecting the intricacies of human behavior, ABA therapists decode the underlying mechanisms that influence social interactions. These foundations provide a solid framework for understanding how specific behaviors manifest and evolve within social contexts. Through empirical research and clinical practice, ABA therapy continuously refines its understanding, adapting interventions to suit individual needs while upholding the integrity of its theoretical underpinnings.
Understanding Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Understanding neurodevelopmental disorders is crucial for providing effective support and intervention to individuals facing these challenges. Neurodevelopmental disorders encompass a range of conditions, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD), attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and intellectual disabilities, among others. These disorders often manifest in early childhood and persist throughout life, impacting various aspects of an individual’s functioning, particularly in communication, social interaction, and behavior. To better grasp the complexities of neurodevelopmental disorders, consider the following:
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Characterized by difficulties in social interaction, communication, and restricted or repetitive behaviors, ASD presents unique challenges in understanding and navigating social cues.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Individuals with ADHD may struggle with impulsivity, hyperactivity, and inattention, affecting their ability to focus and regulate their behavior in social situations.
- Intellectual Disabilities: Intellectual disabilities can affect cognitive functioning, leading to challenges in learning, problem-solving, and adaptive behavior, which can impact social interactions and daily living skills.
- Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD): DCD, also known as dyspraxia, affects motor coordination and can interfere with activities of daily living, including social participation and peer relationships.
- Specific Learning Disorders (SLD): SLDs, such as dyslexia, dyscalculia, and dysgraphia, impact academic skills and may also affect social interactions and self-esteem.
Understanding the nuances of these neurodevelopmental disorders is essential for providing tailored support and interventions that address the unique needs and challenges of individuals affected by these conditions. By fostering awareness, empathy, and inclusion, we can create environments that promote the well-being and success of individuals with neurodevelopmental disorders.
The Role of Behavioral Analysis
Behavioral analysis serves as the cornerstone of ABA therapy, providing a systematic framework for understanding and modifying behavior. By meticulously analyzing observable behaviors and their antecedents and consequences, ABA therapists uncover the underlying mechanisms driving social interactions. Through functional assessments and data-driven approaches, ABA therapy identifies patterns and triggers, guiding the development of targeted interventions. By applying principles of reinforcement and shaping, therapists facilitate meaningful behavior change, paving the way for enhanced social skills and interactions. The meticulous application of behavioral analysis empowers individuals to navigate social nuances with confidence and competence, unlocking a world of possibilities for social connection and fulfillment.
Techniques and Strategies
Within the realm of ABA therapy, a myriad of techniques and strategies are employed to address social challenges and cultivate meaningful interactions. From pivotal response training to discrete trial teaching, each approach is tailored to the unique needs and goals of the individual. Through systematic prompting and reinforcement, ABA therapists scaffold social skills, gradually expanding repertoire and complexity. Social narratives, visual supports, and social scripts provide scaffolding for navigating social scenarios, empowering individuals with strategies for success. By incorporating role-play and peer modeling, ABA therapy fosters social competence in naturalistic settings, ensuring that skills are transferable across contexts.
Generalization and Maintenance
Generalization and Maintenance are crucial aspects of ABA therapy, ensuring that the skills learned during sessions are effectively applied in real-world settings and sustained over time.
- Scaffolding Opportunities: ABA therapists carefully design opportunities for generalization, gradually fading support as skills become internalized.
- Consistent Application: Through systematic programming, individuals practice applying social skills in various contexts to ensure consistency and generalization.
- Maintenance Protocols: ABA therapy incorporates maintenance protocols to sustain gains over time, with periodic reviews and booster sessions to reinforce skills as needed.
- Transferable Skills: By cultivating independence and self-regulation, ABA therapy equips individuals with transferable skills to navigate social situations autonomously.
- Long-term Success: The emphasis on generalization and maintenance fosters long-term success and fulfillment, empowering individuals to thrive in their social environments.
Generalization and Maintenance are integral components of ABA therapy, ensuring that individuals acquire and retain essential social skills for meaningful interactions and long-term success.
Collaboration with Caregivers and Professionals
Collaboration lies at the heart of ABA therapy, bridging the gap between therapists, caregivers, educators, and other professionals in supporting social skill development. Through open communication and shared goals, stakeholders collaborate to create a holistic support network tailored to the individual’s needs. Caregivers play a pivotal role in reinforcing skills outside of therapy sessions, providing opportunities for practice and generalization in naturalistic settings. Educators collaborate with ABA therapists to implement strategies within academic settings, fostering social inclusion and academic success. By fostering a collaborative ethos, ABA therapy maximizes the potential for social growth and development, empowering individuals to thrive within their communities.
Ethical Considerations and Best Practices
Ethical considerations and best practices are fundamental aspects of any ABA therapy program, ensuring the well-being and dignity of individuals undergoing treatment. A commitment to ethical principles guides every facet of practice, from assessment to intervention, fostering trust and integrity within therapeutic relationships. Here are five key points to consider:
- Respect for autonomy: Upholding the individual’s right to self-determination and decision-making, ensuring interventions align with their values and preferences.
- Beneficence: Prioritizing the welfare and best interests of the individual, striving to maximize positive outcomes while minimizing harm.
- Non-maleficence: Avoiding harm and promoting safety through careful assessment, intervention planning, and ongoing monitoring.
- Informed consent: Providing comprehensive information about the nature, risks, and benefits of ABA therapy, empowering individuals and caregivers to make informed decisions.
- Cultural competence: Recognizing and respecting the diversity of backgrounds, beliefs, and experiences, tailoring interventions to be inclusive and culturally sensitive.
In summary, by adhering to ethical guidelines and best practices, ABA therapy cultivates a culture of trust, integrity, and respect, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness and sustainability of social outcomes.
Conclusion
ABA therapy stands as a beacon of hope for individuals navigating the complexities of social interactions, particularly those with neurodevelopmental disorders. With its foundations rooted in behavioral analysis and a commitment to ethical practice, ABA therapy offers tailored interventions that empower individuals to thrive within their communities. From understanding the nuances of behavior to fostering collaboration among caregivers and professionals, ABA therapy prioritizes the well-being and dignity of those undergoing treatment. If you or a loved one could benefit from ABA therapy services, consider reaching out to Positive Solutions Behavior Group LLC, Lakewood Ranch Together, we can embark on a journey towards meaningful social growth and fulfillment.