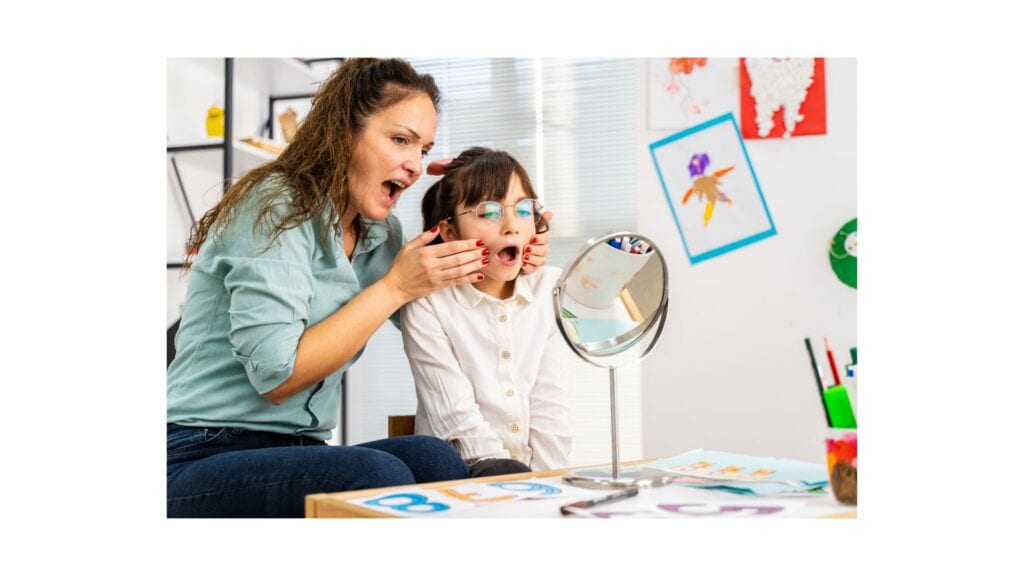
Embarking on a journey toward understanding Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy can be both empowering and overwhelming. Whether you’re a parent seeking the best intervention for your child on the autism spectrum, a practitioner delving into the world of behavioral therapy, or simply someone curious about this transformative approach, you’ve arrived at the right place.
ABA therapy stands as a cornerstone in the realm of behavioral interventions, offering systematic techniques to enhance behaviors crucial for everyday life. Its principles extend beyond autism spectrum disorder (ASD) to encompass various behavioral challenges, ranging from developmental disorders to habit-breaking endeavors.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll navigate through the fundamentals of ABA therapy, unpacking its core principles, methodologies, and applications. Whether you’re a newcomer or seeking to deepen your understanding, this exploration will equip you with the insights needed to appreciate the significance of ABA therapy and its profound impact on individuals, families, and communities.
So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey, unraveling the basics of ABA therapy and discovering the transformative potential it holds for fostering meaningful change.
The Role of ABA Therapy in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy plays a pivotal role in supporting individuals diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), offering tailored interventions to address the diverse challenges they may face. As a comprehensive behavioral approach, ABA therapy is uniquely positioned to target the core symptoms of ASD while fostering skill development and enhancing quality of life. In this exploration, we delve into the specific applications of ABA therapy within the realm of ASD, shedding light on its profound impact on individuals, families, and communities.

Early Intervention and Skill Acquisition
ABA therapy is widely recognized for its effectiveness in early intervention for children with ASD. By utilizing systematic teaching methods and reinforcement techniques, ABA therapists help children acquire essential skills across various domains, including communication, social interaction, self-care, and academic abilities. Early initiation of ABA therapy can significantly enhance developmental outcomes and pave the way for long-term progress.
Behavior Management and Reduction of Challenging Behaviors
Individuals with ASD may exhibit challenging behaviors that interfere with their daily functioning and social interactions. ABA therapy employs evidence-based strategies to identify the underlying triggers of these behaviors through functional behavior assessments (FBA) and develop behavior intervention plans (BIP) aimed at reducing them. By teaching alternative behaviors and providing appropriate reinforcement, ABA therapy helps individuals replace maladaptive behaviors with more adaptive ones, leading to improved self-regulation and overall well-being.
Social Skills Development and Peer Interaction
One of the hallmark features of ASD is difficulty in social communication and interaction. ABA therapy utilizes structured interventions such as social skills training, peer modeling, and role-playing activities to teach individuals with ASD the necessary social skills and etiquette. Through targeted interventions, individuals learn to initiate and maintain conversations, interpret social cues, and engage in reciprocal interactions, thereby improving their social competence and building meaningful relationships.
Functional Independence and Daily Living Skills
ABA therapy equips individuals with ASD with the practical skills needed to navigate daily life with greater independence and confidence. Whether it’s learning self-help skills such as dressing, grooming, and meal preparation or mastering community-based skills such as using public transportation and grocery shopping, ABA interventions focus on promoting functional independence and fostering autonomy in individuals with ASD.
Generalization and Maintenance of Skills
A key objective of ABA therapy is to ensure that learned skills generalize across different environments and are maintained over time. Therapists work collaboratively with individuals, families, and caregivers to promote the transfer of skills learned in therapy sessions to real-life settings such as home, school, and community. By implementing consistent reinforcement strategies and providing ongoing support, ABA therapy facilitates the generalization and long-term retention of acquired skills, thereby maximizing the impact of interventions.
Data Collection and Analysis in ABA Therapy

- Data collection and analysis serve as the backbone of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, providing therapists with invaluable insights into the effectiveness of Interventions and the progress of their clients. By systematically collecting and analyzing data, ABA therapists can make informed decisions, tailor interventions to individual needs, and maximize therapy outcomes. In this exploration, we delve into the significance of data collection and analysis in ABA therapy, highlighting key points that underscore its essential role in driving evidence-based practice and promoting positive behavior change.
- Objective Measurement: Data collection in ABA therapy relies on objective measurement of behavior, allowing therapists to quantify observable actions and track progress over time. This involves defining target behaviors in clear and measurable terms, establishing reliable methods for recording data, and ensuring consistency in data collection procedures across sessions.
- Baseline Assessment: Before implementing interventions, ABA therapists conduct baseline assessments to establish a benchmark against which progress can be measured. Baseline data provide valuable information about the frequency, intensity, and duration of target behaviors before intervention, serving as a reference point for evaluating the effectiveness of subsequent interventions.
- Continuous Monitoring: Data collection in ABA therapy is an ongoing process that involves continuous monitoring of target behaviors throughout the course of treatment. Therapists systematically collect data during therapy sessions, using various recording methods such as frequency counts, duration recording, interval recording, and event recording to capture relevant behavioral data.
- Visual Representation: Data analysis in ABA therapy often involves visual representation of data through graphs and charts, allowing therapists to identify patterns, trends, and changes in behavior over time. Visual analysis facilitates the interpretation of data, enabling therapists to make data-driven decisions and modify interventions as needed to achieve desired outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding the fundamentals of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is crucial for individuals seeking effective interventions for behavioral challenges. At Positive Solutions Behavior Group LLC, we prioritize providing comprehensive information and support to our clients in Mason, Ohio, and beyond. By equipping individuals with the knowledge outlined in our guide, we aim to empower families and caregivers to make informed decisions regarding the well-being and development of their loved ones. Through our commitment to excellence and client-centered approach, we strive to promote positive outcomes and enhance the quality of life for those we serve. For inquiries, please contact us at 859-282-0400.