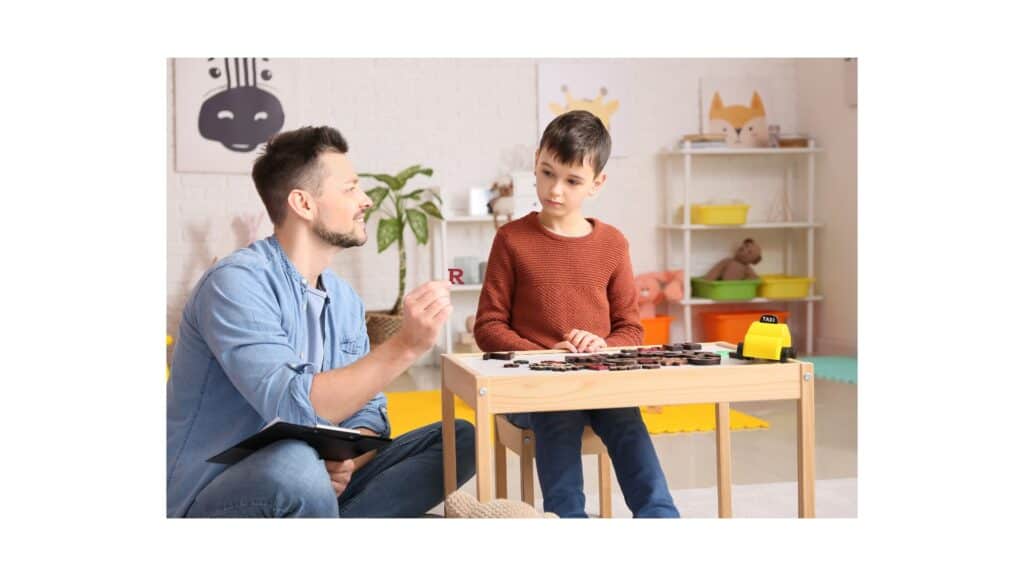
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy has long been recognized as a cornerstone in the treatment of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), helping individuals develop vital skills and navigate the complexities of daily life. However, the scope of ABA therapy extends far beyond its association with autism. In recent years, its efficacy in addressing a wide array of conditions beyond ASD has garnered attention from researchers, practitioners, and families alike.
In this exploration, we delve into the lesser-known territories of ABA therapy, shedding light on its application in treating various conditions beyond autism. From attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) to obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and beyond, ABA therapy offers a versatile toolkit that can be tailored to meet the unique needs of individuals across different diagnoses.
Join us as we uncover the multifaceted nature of ABA therapy, unveiling its potential to transform lives and pave the way for a more inclusive and supportive future. Whether you’re a parent seeking options for your child’s developmental challenges or a professional curious about the expanding landscape of behavioral interventions, this journey promises to be enlightening and informative.
Prepare to embark on a journey that transcends the boundaries of traditional perceptions, as we navigate the landscape of ABA therapy and discover its transformative impact on individuals beyond the realm of autism.
Navigating Behavioral Challenges in Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Understanding Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Neurodevelopmental disorders encompass conditions such as Tourette syndrome, fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD), Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS), and others. These disorders typically manifest early in life and are characterized by atypical brain development, leading to a range of cognitive, behavioral, and motor impairments. Each disorder presents unique challenges, but many share common features such as difficulties with impulse control, repetitive behaviors, and social communication deficits.

The Role of ABA Therapy
ABA therapy is a structured, evidence-based approach that focuses on understanding and modifying behavior patterns to improve overall functioning and quality of life. While traditionally associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), ABA techniques have been increasingly applied to address the behavioral challenges associated with various neurodevelopmental disorders.
Tailoring Interventions to Individual Needs
One of the strengths of ABA therapy lies in its ability to tailor interventions to meet the specific needs of each individual. ABA therapists conduct thorough assessments to identify target behaviors, establish baseline data, and develop personalized intervention plans. These plans often involve breaking down complex skills into smaller, achievable steps and using reinforcement strategies to encourage desired behaviors.
Addressing Impulse Control in Tourette Syndrome
Tourette syndrome is characterized by involuntary motor and vocal tics, as well as associated behavioral challenges such as impulsivity and difficulty with emotional regulation. ABA therapy can help individuals with Tourette syndrome learn to manage their impulses, reduce the frequency and intensity of tics, and develop alternative coping strategies for dealing with stressors.
Supporting Executive Functioning in Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD) result from prenatal exposure to alcohol and can lead to a range of cognitive and behavioral impairments, including difficulties with executive functioning, impulse control, and adaptive skills. ABA interventions target these areas by teaching individuals with FASD strategies for planning, problem-solving, and self-regulation.
Promoting Structured Routines in Prader-Willi Syndrome
Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) is a genetic disorder characterized by hyperphagia (excessive eating), developmental delays, and behavioral issues such as obsessive-compulsive tendencies and temper outbursts. ABA therapy emphasizes the establishment of structured routines, reinforcement of appropriate eating behaviors, and implementation of strategies to manage compulsive behaviors and emotional dysregulation.
Collaborating with Multidisciplinary Teams
In addressing the complex needs of individuals with neurodevelopmental disorders, ABA therapists often collaborate closely with multidisciplinary teams comprising physicians, psychologists, speech therapists, and other professionals. This interdisciplinary approach ensures comprehensive assessment, treatment planning, and ongoing support for individuals and their families.
Introduction: Building Social Skills Beyond Autism Spectrum

- Understanding the Importance of Social Skills: Social skills encompass a broad range of abilities, including effective communication, empathy, cooperation, and conflict resolution. These skills are essential for forming meaningful relationships, succeeding in academic and professional settings, and participating fully in social activities.
- Identifying Social Challenges Across Diagnoses: While individuals with autism spectrum disorder may face distinct social challenges such as difficulty with nonverbal cues or maintaining eye contact, other neurodevelopmental and behavioral disorders also present obstacles to social interaction. These may include ADHD-related impulsivity, anxiety-related social avoidance, or difficulties with perspective-taking in conditions like oppositional defiant disorder (ODD).
- Applying ABA Principles to Social Skills Development: ABA therapy offers a systematic approach to teaching and reinforcing social skills, regardless of the underlying diagnosis. Through techniques such as modeling, role-playing, and social stories, individuals can learn and practice appropriate social behaviors in structured settings.
- Tailoring Interventions to Individual Needs: Just as ABA therapy customizes interventions for other areas of development, such as language or self-help skills, social skills training is tailored to the unique strengths and challenges of each individual. This personalized approach maximizes effectiveness and promotes meaningful progress.
- Promoting Inclusion and Peer Interaction: A crucial aspect of social skills development is the opportunity for individuals to engage with peers in inclusive environments. ABA therapists facilitate opportunities for social interaction, providing support and guidance as individuals navigate social situations and build relationships.
Conclusion
Positive Solutions Behavior Group LLC, based in Mason, Ohio, USA, offers comprehensive Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy not only for individuals with autism but also for a spectrum of other conditions. With a commitment to personalized care and evidence-based interventions, we strive to empower individuals and families by fostering positive behavioral changes and improving quality of life. Through our tailored approach and dedicated team, we aim to continue serving as a beacon of support and progress for individuals with diverse needs, underscoring our dedication to inclusivity and holistic wellness. For inquiries, please contact us at 859-282-0400.