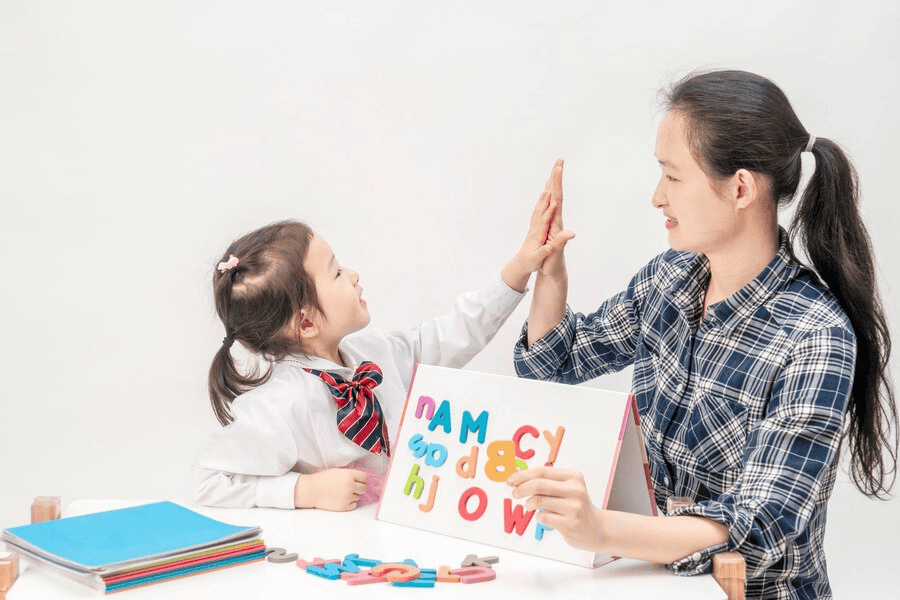
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) in educational settings focuses on understanding and improving student behavior through evidence-based strategies. It helps educators tailor their teaching methods to meet the unique needs of each learner, promoting positive behaviors and minimizing challenging ones. By analyzing data on student performance, teachers can implement interventions that support skill development and enhance engagement. ABA fosters a collaborative environment, encouraging communication between teachers, students, and families. Ultimately, this approach empowers students to succeed academically and socially, paving the way for lifelong learning and personal growth.
Understanding ABA Principles
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is grounded in several key principles, including reinforcement, punishment, and behavior modification. Reinforcement strengthens desired behaviors, while punishment aims to decrease undesirable actions. Educators apply these principles to create structured environments where positive behaviors are consistently rewarded, leading to improved student outcomes. By understanding how behavior works, teachers can craft interventions that resonate with individual students, enabling them to thrive both academically and socially. ABA emphasizes the importance of data-driven decision-making, ensuring that interventions are tailored and effective.
Here are five H3 subheadings, each with a 70-word paragraph explaining key aspects of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA):

Core Principles of ABA
At the heart of Applied Behavior Analysis are core principles that guide its application in educational settings. These include reinforcement, which encourages positive behaviors, and punishment, which discourages negative actions. Understanding these principles allows educators to implement strategies that can shape behavior effectively. This foundational knowledge empowers teachers to create a structured environment that promotes student success through targeted interventions and consistent reinforcement of desired behaviors.
Behavioral Assessment Techniques
Behavioral assessment techniques are crucial for identifying the specific needs of students. These assessments help educators analyze student behavior and determine the most effective interventions. Techniques such as direct observation, functional behavior assessments, and data collection provide insights into behavior patterns. By using these methods, teachers can develop personalized strategies that address the unique challenges faced by each student, ultimately promoting a positive learning experience and enhancing academic achievement.
Reinforcement Strategies for Positive Behavior
Reinforcement strategies are essential for encouraging positive behavior among students. These strategies may involve verbal praise, tangible rewards, or token systems that recognize and celebrate students’ achievements. By consistently applying reinforcement, educators can create an environment that fosters motivation and engagement. The effectiveness of reinforcement strategies hinges on their timely application and alignment with individual student preferences, ensuring that students feel valued and understood in their learning journey.
Data Collection and Analysis in ABA
Data collection and analysis play a vital role in the effectiveness of Applied Behavior Analysis. Educators systematically track student behavior to evaluate the success of interventions. This ongoing assessment allows teachers to make informed decisions and adjust strategies as needed. By focusing on measurable outcomes, educators can identify trends, celebrate successes, and pinpoint areas for improvement. This data-driven approach fosters accountability and ensures that every student receives the support necessary to thrive.
Collaboration with Stakeholders
Collaboration with stakeholders, including families and other educators, enhances the effectiveness of ABA interventions. By involving parents and guardians, teachers can create a consistent approach to behavior management that extends beyond the classroom. Regular communication ensures that families understand intervention goals and can reinforce strategies at home. Building partnerships with other educators also promotes sharing best practices, fostering a supportive community that is committed to helping students achieve their full potential.
Tailoring Interventions to Individual Needs
Every student is unique, and ABA allows educators to tailor interventions specifically to individual needs. By conducting thorough assessments, teachers can identify the specific behaviors that need addressing and the best strategies to implement. For example, some students may respond well to visual supports, while others may thrive with verbal prompts. This personalized approach not only enhances student engagement but also promotes a sense of ownership over their learning process. By recognizing and responding to individual differences, educators can create a more inclusive and effective classroom environment.
Enhancing Classroom Management
Classroom management is crucial for a productive learning environment, and ABA provides valuable strategies to enhance it. Teachers can establish clear expectations and consistently apply consequences, which helps create a structured atmosphere where students feel secure. Utilizing ABA techniques, such as token economies or visual schedules, can reinforce appropriate behaviors and minimize disruptions. These strategies not only promote a positive classroom culture but also encourage students to take responsibility for their actions. Ultimately, effective classroom management leads to improved academic performance and a more harmonious learning environment.
Fostering Social Skills Development
Social skills are essential for students’ overall development, and ABA plays a pivotal role in teaching these skills in educational settings. Through structured social skills training, educators can help students learn how to communicate effectively, share, and resolve conflicts. Using role-playing, modeling, and reinforcement, teachers can create opportunities for students to practice these skills in a safe environment. By fostering social competence, ABA not only enhances peer relationships but also builds students’ confidence, preparing them for interactions both inside and outside the classroom.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Incorporating data into educational practices is a cornerstone of ABA. Teachers collect and analyze data on student behavior to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions and make informed decisions. This process involves tracking progress over time and adjusting strategies based on what works best for each student. By employing data-driven decision-making, educators can identify trends, recognize areas for improvement, and celebrate successes. This approach not only fosters accountability but also empowers teachers to optimize their practices, ensuring that every student receives the support they need to succeed.
Collaboration with Families
Collaboration between educators and families is essential for the success of ABA interventions. By involving parents and guardians in the process, teachers can create a unified approach to addressing behavioral concerns. Regular communication ensures that families understand the goals of the interventions and can reinforce strategies at home. This partnership fosters a supportive network that enhances student progress and strengthens relationships between school and home. When families are engaged in their child’s education, students are more likely to thrive academically and socially, leading to positive long-term outcomes.
Promoting Inclusion in the Classroom
ABA promotes inclusive practices by helping educators support students with diverse needs. By applying behavior analysis techniques, teachers can create an environment that accommodates all learners, including those with special needs. This approach involves modifying teaching methods, materials, and assessments to ensure every student has equitable access to the curriculum. Inclusive classrooms foster acceptance and understanding among peers, creating a more harmonious learning environment. By embracing diversity and applying ABA principles, educators can empower all students to reach their full potential.
Preparing Students for Lifelong Success
The ultimate goal of ABA in educational settings is to equip students with skills that extend beyond the classroom. By focusing on behavioral and social skill development, educators help students build resilience and adaptability. These skills are crucial for navigating future challenges, whether in higher education, the workplace, or personal relationships. ABA prepares students to set and achieve their goals, fostering a sense of independence and self-efficacy. By instilling these essential skills, educators not only promote academic success but also empower students to thrive in all aspects of life.
Conclusion
Incorporating Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) in educational settings has proven to be a transformative approach for students with diverse learning needs. By focusing on data-driven strategies, ABA empowers educators and parents to foster positive behavioral changes, enhance learning outcomes, and create inclusive environments. As we continue to explore the potential of ABA in education, collaboration among stakeholders remains vital for achieving long-term success.
For more information on how Positive Solutions Behavior Group LLC can support your educational initiatives in Mason, OH, please reach out to us at **859-282-0400**. Together, we can make a meaningful difference in the lives of students and families in our community.