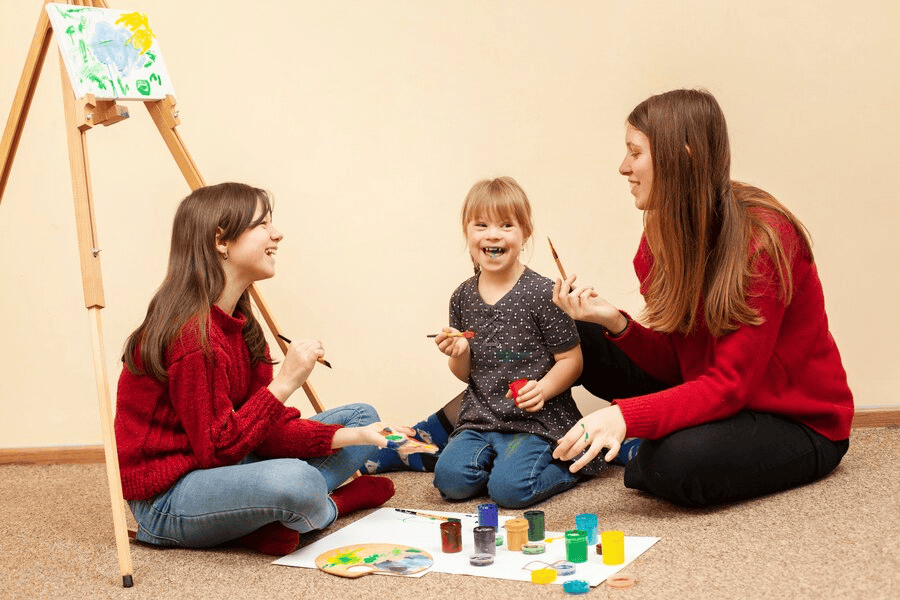
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) can be a powerful tool for helping children manage anxiety. By breaking down behaviors into smaller, observable components, ABA allows therapists to understand the triggers of a child’s anxiety and develop strategies to reduce it. Through positive reinforcement and gradual exposure, children can learn coping skills that decrease anxious responses over time. ABA also involves parents and caregivers, ensuring consistency and support across environments. This personalized approach helps children build confidence and navigate anxiety in a structured, supportive way.
Understanding Anxiety in Children
Anxiety in children can manifest in various ways, including excessive worry, avoidance behaviors, and physical symptoms like stomach aches. Recognizing the signs of anxiety is crucial for parents and educators to provide timely support. Factors contributing to childhood anxiety may include genetics, environmental stressors, and traumatic experiences. Understanding these elements can help caregivers identify the underlying issues affecting a child’s emotional well-being. By acknowledging and addressing anxiety early on, parents can create a nurturing environment that fosters resilience and healthy coping strategies, paving the way for better emotional regulation in the future.

Signs of Anxiety in Children
Identifying signs of anxiety in children is essential for effective intervention. Common indicators include excessive worrying, irritability, and social withdrawal. Physical symptoms, such as headaches or stomach aches, can also arise when a child is anxious. Parents and educators should be vigilant in recognizing these behaviors to provide timely support, helping children feel safe and understood. Early recognition allows caregivers to address anxiety proactively, fostering a healthier emotional environment.
Causes of Childhood Anxiety
Various factors can contribute to childhood anxiety, including genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and exposure to trauma. Children may inherit anxiety tendencies from family members or face stressors such as academic pressure and bullying. Understanding these causes is vital for caregivers, as it helps them address the root of the problem rather than just the symptoms. By recognizing these factors, parents can create a supportive atmosphere that nurtures emotional well-being.
The Impact of Early Intervention
Early intervention is crucial in managing childhood anxiety. When parents and educators act promptly, children are more likely to develop healthy coping mechanisms. Early support can prevent anxiety from escalating, allowing children to navigate challenges with greater ease. This proactive approach not only improves emotional regulation but also enhances overall well-being. Creating a supportive environment encourages children to express their feelings and seek help when needed.
Creating a Nurturing Environment
A nurturing environment is fundamental for helping children cope with anxiety. Parents can foster a sense of safety by providing consistent routines and open communication. Encouraging children to express their feelings and concerns helps validate their experiences, making them feel heard and supported. Establishing a positive home atmosphere contributes significantly to emotional resilience, enabling children to tackle anxiety with greater confidence and develop healthy coping strategies.
Fostering Resilience in Children
Fostering resilience is essential for helping children manage anxiety effectively. By teaching problem-solving skills and promoting a growth mindset, parents can empower their children to face challenges head-on. Encouraging healthy relationships and social interactions also plays a vital role in building resilience. When children learn to cope with setbacks and understand that anxiety is a manageable part of life, they are better equipped to navigate future challenges with confidence.
The Role of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a therapeutic approach that focuses on modifying behavior through principles of learning and behaviorism. It emphasizes the importance of observable behavior, allowing therapists to analyze and understand specific actions that contribute to anxiety in children. By identifying triggers and reinforcing positive behaviors, ABA helps create a structured environment where children can develop coping mechanisms. This method is particularly effective for children with autism spectrum disorder but can benefit any child struggling with anxiety. ABA’s systematic approach promotes positive change, enhancing emotional well-being and adaptive functioning.
Identifying Triggers Through Behavior Analysis
A critical step in using ABA to reduce anxiety is identifying the specific triggers that lead to anxious behaviors. Therapists work closely with children and their families to observe patterns and pinpoint situations that provoke anxiety. This process may involve analyzing a child’s responses in various settings, such as school or home. By understanding these triggers, therapists can develop targeted interventions that address the root causes of anxiety. This tailored approach allows children to confront their fears gradually, fostering resilience and confidence while reducing the intensity of their anxious responses over time.
Positive Reinforcement Techniques
Positive reinforcement is a cornerstone of ABA and plays a vital role in reducing anxiety in children. By rewarding positive behaviors with praise, rewards, or other incentives, therapists encourage children to engage in more adaptive responses to anxiety-provoking situations. For instance, if a child successfully manages their anxiety in a challenging social setting, they may receive a small reward or acknowledgment. This reinforcement not only boosts self-esteem but also teaches children that they can effectively cope with their fears. Over time, this creates a positive feedback loop, reinforcing healthier behaviors and reducing anxiety.
Gradual Exposure Strategies
Gradual exposure is a key component of ABA, allowing children to confront their fears in a controlled and manageable way. This technique involves exposing the child to anxiety-inducing situations gradually, starting with less challenging scenarios before progressing to more difficult ones. For example, if a child has a fear of speaking in front of others, they might first practice speaking in front of a trusted family member before advancing to a small group. This step-by-step approach helps children build confidence, as they learn that they can face their fears and manage their anxiety effectively over time.
The Importance of Parent Involvement
Involving parents and caregivers in the ABA process is essential for achieving lasting results in reducing anxiety. Parents play a pivotal role in reinforcing positive behaviors and implementing strategies learned in therapy at home. Training sessions can equip parents with the tools to support their child’s progress, ensuring consistency in managing anxiety across different environments. Additionally, parent involvement fosters stronger communication and understanding between the child and their caregivers, creating a supportive atmosphere where the child feels safe to express their feelings and work on coping strategies.
Building Coping Skills for the Future
One of the primary goals of using ABA for anxiety reduction is to equip children with effective coping skills they can use throughout their lives. As children learn to identify their feelings and manage their responses to anxiety-provoking situations, they develop resilience and emotional intelligence. Techniques such as deep breathing, visualization, and positive self-talk can be integrated into therapy sessions and practiced at home. By instilling these skills early on, children are better prepared to navigate challenges in the future, fostering a sense of empowerment and self-efficacy in managing their emotions.
Measuring Progress and Success
Measuring progress in ABA therapy is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing anxiety. Therapists typically use data collection methods, such as frequency counts or rating scales, to track changes in behavior over time. Regular assessments help identify areas of improvement and adjust strategies as needed. By celebrating small victories, both therapists and families can motivate children to continue working toward their goals. This focus on measurable success not only enhances the therapy experience but also reinforces the child’s belief in their ability to overcome anxiety and achieve personal growth.
Conclusion
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) offers a structured and effective approach to help reduce anxiety in children. By understanding and modifying behaviors, ABA empowers children to develop coping strategies and improve their emotional well-being. With tailored interventions, families can witness significant progress in their child’s ability to manage anxiety, leading to a more fulfilling life.
At Positive Solutions Behavior Group LLC in Beavercreek, OH, our dedicated team is committed to supporting children and families through these challenges. For more information, please contact us at 859-282-0400 to learn how we can assist your child in achieving greater emotional resilience.