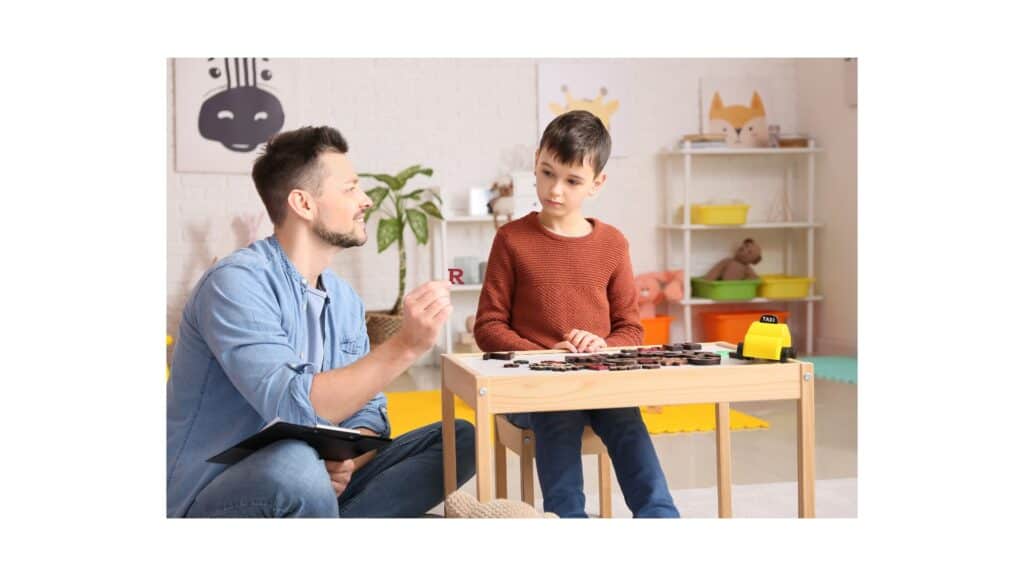
Navigating the complex landscape of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) often feels like deciphering an intricate puzzle. Among the myriad of approaches aimed at assisting individuals with ASD, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) stands out for its emphasis on social strategies. At the heart of ABA lies a structured framework designed to enhance communication skills, social interactions, and behavioral patterns in those with autism. However, understanding the nuances of ABA’s social strategies requires more than surface-level comprehension. Delving into its methodologies, principles, and real-world applications unveils a deeper understanding of how ABA fosters social development in individuals on the autism spectrum. Join us on this exploration as we decode the intricacies of ABA’s social strategies and their impact on the lives of those with autism.
The Fundamentals of ABA: Building Blocks for Social Growth
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) serves as a cornerstone in the realm of autism intervention, particularly in fostering social growth. At its core, ABA operates on the principles of understanding behavior through observation, breaking it down into manageable components, and systematically implementing interventions to bring about positive change. In the context of social development, ABA lays the groundwork by identifying specific social skills deficits and designing structured interventions to address them. By focusing on fundamental behaviors such as eye contact, turn-taking, and understanding social cues, ABA provides individuals on the autism spectrum with the foundational skills necessary for meaningful social interactions.
Targeting Social Skills: A Closer Look at ABA's Approach
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) meticulously targets social skills for individuals with autism spectrum disorders (ASD), employing evidence-based techniques to foster growth. Through tailored strategies like prompting and reinforcement, ABA facilitates the acquisition of desired behaviors in structured sessions, enabling real-world application.
- Comprehensive Assessment: ABA conducts thorough evaluations to pinpoint specific social skills deficits.
- Individualized Interventions: Tailored strategies are developed to address each individual’s unique needs and challenges.
- Evidence-Based Techniques: ABA employs proven methods such as prompting, modeling, and reinforcement to teach and reinforce desired social behaviors.
- Structured Sessions: ABA sessions are carefully structured to provide ample opportunities for practice and generalization of social skills.
- Real-World Application: ABA interventions are designed to facilitate the application of social skills in everyday life contexts.
In summary, ABA’s approach to targeting social skills is comprehensive, individualized, and evidence-based, aiming to empower individuals with ASD to thrive socially in various settings. Through structured sessions and real-world application, ABA facilitates the acquisition and generalization of social skills, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for individuals with autism spectrum disorders.
Behavior Modification: Shaping Social Interactions Through Positive Reinforcement
Central to ABA’s effectiveness in shaping social interactions is the principle of positive reinforcement. By strategically reinforcing desired social behaviors with rewards or praise, ABA practitioners facilitate the acquisition and maintenance of these behaviors over time. Through a process known as behavior modification, individuals with autism learn to associate positive outcomes with specific social actions, thus increasing the likelihood of their recurrence. Moreover, ABA emphasizes the importance of consistency and predictability in reinforcement schedules to optimize learning outcomes. By harnessing the power of positive reinforcement, ABA empowers individuals on the autism spectrum to navigate social situations with confidence and competence.
From Theory to Practice: Implementing ABA Social Strategies in Daily Life
Implementing ABA social strategies in daily life requires a seamless transition from theoretical understanding to practical application. A key aspect of this process involves collaboration between behavior analysts, caregivers, educators, and other stakeholders to ensure consistency and continuity across different settings. ABA interventions are carefully designed to be accessible and adaptable, allowing individuals with autism to practice their social skills in naturalistic environments such as home, school, and community settings. Furthermore, ongoing data collection and analysis enable practitioners to monitor progress, make necessary adjustments, and fine-tune interventions to better suit the individual’s evolving needs. Through this holistic approach, ABA social strategies become integrated into the fabric of everyday life, fostering sustainable social growth and development.
Individualized Approaches: Tailoring ABA Interventions to Meet Social Needs
Individualized approaches in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) address diverse social needs by conducting comprehensive assessments to identify strengths, weaknesses, and goals. Tailored intervention plans adapt to changes over time, empowering individuals to navigate social interactions confidently.
- Comprehensive assessments: Identify individual strengths and weaknesses in social interaction.
- Personalized intervention plans: Tailored to address specific social needs and goals.
- Flexibility and responsiveness: Interventions adapt to changes over time.
- Empowerment through personalized strategies: Individuals gain confidence in social interactions.
- Maximizing social competence: Individualized approaches foster meaningful progress and growth.
Individualized approaches in ABA are instrumental in maximizing social competence and empowering individuals with autism to thrive socially. By tailoring interventions to meet specific needs and goals, ABA promotes confidence and success in navigating social interactions.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Techniques in ABA for Enhancing Social Competence
While ABA’s foundational principles lay the groundwork for social growth, advanced techniques further enhance social competence in individuals on the autism spectrum. These techniques may include video modeling, social stories, role-playing, and peer-mediated interventions, among others. By leveraging innovative approaches, ABA practitioners provide individuals with autism opportunities to generalize their social skills across a variety of social contexts and interactions. Additionally, advanced techniques often incorporate strategies for promoting self-awareness, self-regulation, and perspective-taking, fostering deeper understanding and appreciation of social norms and expectations. Through continuous exploration and refinement of advanced techniques, ABA continues to push the boundaries of social intervention, unlocking new possibilities for individuals with autism.
Evaluating Effectiveness: Measuring the Impact of ABA Social Strategies on Autistic Individuals
Evaluating the effectiveness of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) social strategies is crucial for understanding their impact on autistic individuals. Through rigorous assessment and analysis, ABA practitioners gauge progress and tailor interventions to meet unique needs. Utilizing various tools, ABA evaluates social behaviors and adjusts strategies accordingly to maximize outcomes and foster meaningful social growth.
- Comprehensive Assessment: ABA conducts thorough evaluations to identify social skills deficits and strengths in autistic individuals.
- Data-Driven Decisions: ABA practitioners collect and analyze data on social behaviors to inform intervention strategies.
- Tailored Interventions: Based on assessment findings, ABA develops individualized intervention plans to address specific social needs.
- Ongoing Monitoring: ABA employs continuous evaluation to track progress and make adjustments as needed throughout the intervention process.
- Maximizing Outcomes: By leveraging assessment data, ABA aims to optimize outcomes and enhance the quality of life for autistic individuals.
For those seeking effective support for autism spectrum disorders, ABA’s commitment to evaluating effectiveness ensures tailored interventions and sustainable social growth.
Conclusion
Positive Solutions Behavior Group LLC Beavercreek, provides invaluable resources for individuals with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) through its implementation of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) techniques. ABA serves as a robust framework for fostering social growth by targeting specific skills, employing behavior modification techniques, and tailoring interventions to individual needs. By bridging the gap between theory and practice, ABA strategies seamlessly integrate into daily life, promoting sustainable social development. Furthermore, the utilization of advanced techniques and rigorous evaluation ensures continuous improvement and maximizes outcomes for individuals with autism. For those seeking effective interventions and support for ASD, Positive Solutions Behavior Group LLC offers comprehensive services to empower individuals and enhance their quality of life. Contact them today to embark on the journey towards social growth and well-being.