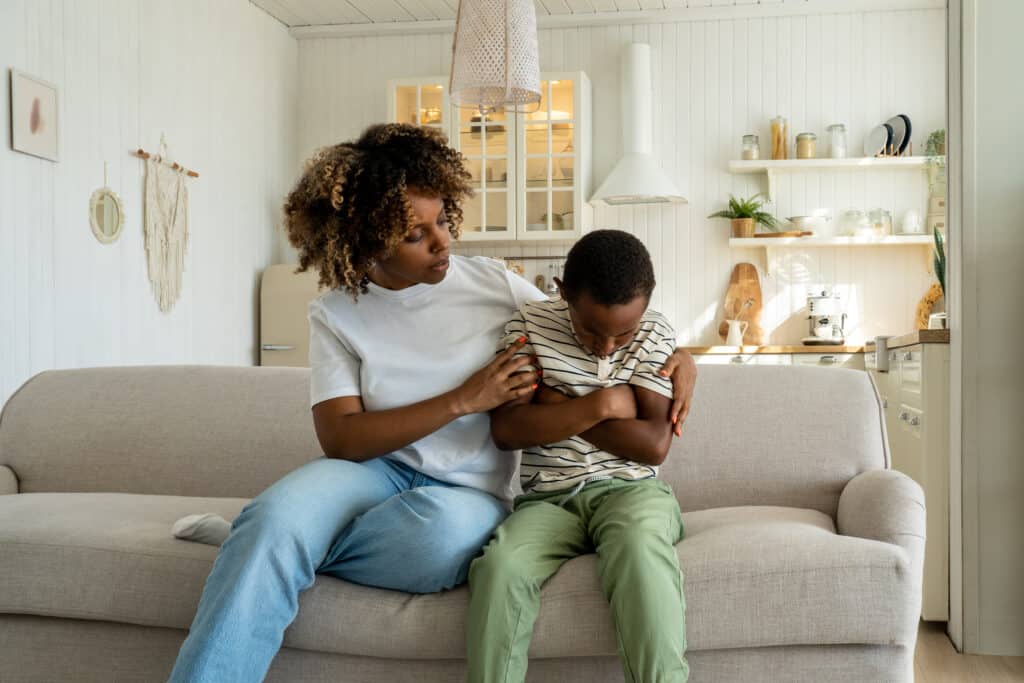
Navigating the intricate landscape of social interaction can be particularly challenging for individuals on the autism spectrum. Understanding and interpreting social cues, navigating conversations, and building meaningful connections are skills that often require intentional guidance and support. This is where Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) steps in as a valuable tool. ABA, a widely recognized therapeutic approach, offers insights and strategies tailored to address the unique social challenges faced by individuals with autism. In this blog series, we delve into the intersection of ABA and social skills development, exploring practical tips, research findings, success stories, and the latest advancements in the field. Join us as we embark on a journey to unlock the potential of individuals with autism through ABA insights.
Understanding Social Skill Deficits in Autism
Individuals on the autism spectrum often face challenges in understanding and engaging in social interactions. These deficits can manifest in various ways, including difficulty interpreting nonverbal cues, understanding social norms, and initiating or maintaining conversations. Moreover, individuals with autism may struggle with perspective-taking, empathy, and forming friendships, which are fundamental aspects of social interaction. Understanding these deficits is crucial for developing effective interventions tailored to address the specific needs of individuals with autism, promoting their social growth and enhancing their quality of life.
The Role of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) in Social Skills Development
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) plays a pivotal role in addressing social skills deficits in individuals with autism. ABA offers a systematic approach to understanding behavior and its underlying causes, making it particularly effective for targeting social challenges. Through ABA interventions, therapists can assess the individual’s social strengths and weaknesses, identify target behaviors, and implement evidence-based strategies to teach and reinforce social skills. By breaking down complex social behaviors into manageable steps and providing structured practice opportunities, ABA helps individuals with autism develop essential social competencies and improve their overall social functioning.
Targeting Specific Social Challenges: ABA Strategies
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) employs a variety of strategies to target specific social challenges faced by individuals with autism. These strategies often involve breaking down social skills into smaller, more manageable components and teaching them systematically through structured activities and exercises. ABA techniques such as modeling, prompting, role-playing, and social stories are commonly used to teach social skills in a structured and supportive environment. Additionally, ABA interventions focus on reinforcement, providing positive feedback and rewards to encourage the acquisition and maintenance of desired social behaviors. By targeting specific social challenges with tailored strategies, ABA helps individuals with autism develop the skills they need to navigate social interactions successfully.
Building Social Communication: ABA Techniques for Individuals with Autism
Effective social communication is fundamental for individuals with autism to navigate the complexities of social interactions. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) offers a structured approach to develop these crucial skills, empowering individuals with autism to express themselves and connect with others more confidently.
- Visual supports: ABA utilizes visual aids such as picture schedules and communication boards to enhance understanding and facilitate communication.
- Role-playing: Engaging in role-playing scenarios allows individuals to practice social interactions in a safe and supportive environment, improving communication skills.
- Verbal and nonverbal cues: ABA techniques focus on teaching individuals with autism to interpret both verbal and nonverbal cues, such as body language and facial expressions, aiding in effective communication.
- Conversational turn-taking: Through structured activities and practice sessions, individuals learn the importance of taking turns in conversations, fostering reciprocal communication.
- Reinforcement: ABA interventions emphasize positive reinforcement to encourage the use of appropriate communication skills, reinforcing desired behaviors and promoting social communication development.
ABA techniques provide invaluable tools and strategies for individuals with autism to build and enhance their social communication skills. By incorporating visual supports, role-playing, and reinforcement, ABA fosters effective communication and meaningful connections, empowering individuals to thrive in social interactions.
Addressing Social Anxiety and Sensory Sensitivities through ABA
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) interventions not only target social skills deficits but also address associated challenges such as social anxiety and sensory sensitivities in individuals with autism. ABA techniques, such as desensitization and systematic desensitization, are used to gradually expose individuals to social situations or sensory stimuli that may trigger anxiety or discomfort. By providing opportunities for exposure in a controlled and supportive environment, ABA helps individuals with autism learn to manage their anxiety and sensory sensitivities more effectively. Additionally, ABA teaches coping strategies and relaxation techniques to help individuals regulate their emotions and responses in social and sensory situations, promoting greater confidence and comfort in social interactions.
Promoting Social Inclusion: ABA Community Integration Programs
Promoting Social Inclusion through ABA Community Integration Programs is essential for individuals with autism. These programs offer structured opportunities for real-world social skill practice, fostering belonging and acceptance. ABA therapists work closely with participants and families, creating tailored interventions to support social integration.
- Structured Social Activities: Engage participants in structured group activities designed to promote social interaction and communication skills.
- Community Outings: Provide opportunities for individuals to practice social skills in various community settings, such as parks, libraries, and local businesses.
- Peer Interaction: Facilitate peer interactions and friendships through guided activities and collaborative projects.
- Skill Generalization: Encourage the generalization of social skills learned in therapy sessions to real-life situations, promoting independence and confidence.
- Family Involvement: Involve families in the intervention process, providing support and resources to reinforce social skill development at home and in the community.
ABA Community Integration Programs play a vital role in promoting social inclusion and enhancing the quality of life for individuals with autism. Through structured interventions and community engagement, participants develop essential social skills, forge meaningful connections, and experience a sense of belonging within their communities.
Measuring Progress: Outcome Assessment in ABA Social Skills Interventions
Measuring progress in ABA social skills interventions is crucial for evaluating effectiveness and tailoring support for individuals with autism. Outcome assessment methods, including systematic observation, behavior tracking, and standardized assessments, provide valuable insights into social competency development over time. By tracking measurable outcomes such as improvements in social communication and community engagement, therapists can make informed decisions about treatment planning and goal setting, maximizing intervention effectiveness.
Outcome Assessment Methods in ABA Social Skills Interventions
- Systematic Observation: Therapists observe and document social behaviors in various settings to track progress and identify areas of improvement.
- Behavior Tracking: Utilizing data collection tools to monitor target behaviors and measure changes over time, allowing for data-driven decision-making.
- Standardized Assessments: Administering standardized tests and assessments to quantify social skills development and compare progress against normative data.
Benefits of Measuring Progress in ABA Interventions
- Personalized Intervention Planning: Allows for tailored interventions based on individual strengths, weaknesses, and progress.
- Evidence-Based Decision-Making: Provides data-driven insights for adjusting intervention strategies and setting realistic goals.
- Accountability and Transparency: Demonstrates the effectiveness of ABA interventions to stakeholders, including families, educators, and funding agencies.
Outcome assessment plays a crucial role in ABA social skills interventions by facilitating informed decision-making, ensuring accountability, and promoting personalized support for individuals with autism. By systematically measuring progress, therapists can empower individuals to reach their full potential and achieve meaningful social outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing social skill deficits in autism is vital for the well-being and development of individuals on the spectrum. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) emerges as a powerful tool in this journey, offering structured interventions tailored to target specific social challenges. By utilizing ABA strategies, individuals with autism can build essential social communication skills, manage social anxiety and sensory sensitivities, and actively participate in community integration programs. Moreover, the systematic measurement of progress ensures that interventions are effective and personalized, maximizing social growth and enhancing overall quality of life. For those seeking support in addressing social skills deficits, Positive Solutions Behavior Group LLC stands ready to assist at Beavercreek, Contact them today to embark on the journey towards positive social development.