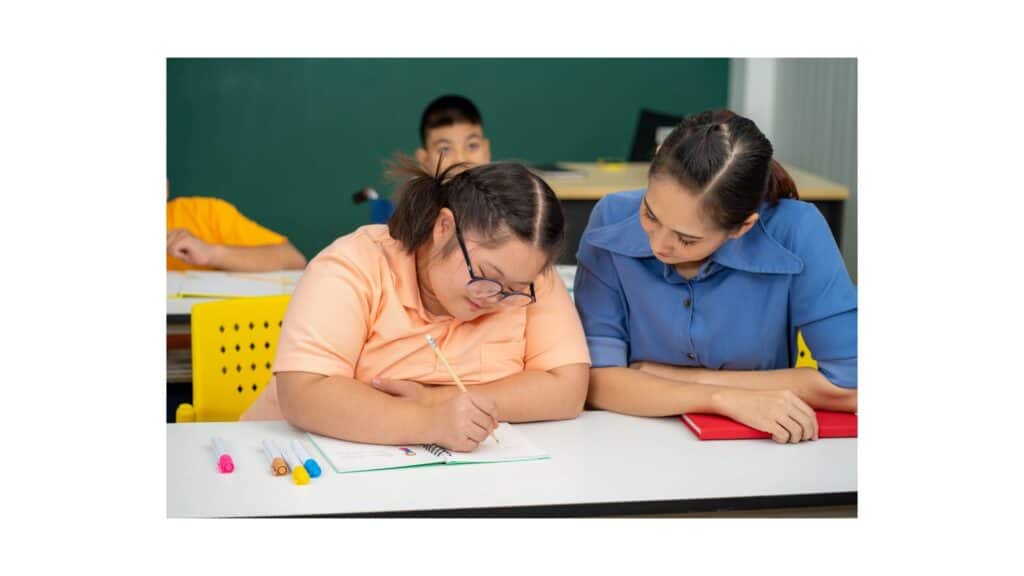
Navigating social interactions can be a complex journey for anyone, but for individuals on the autism spectrum, it often presents unique challenges. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) affects how a person perceives and socializes with others, making it essential to explore effective interventions like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. ABA therapy has gained recognition for its role in addressing various aspects of ASD, including social dynamics. By breaking down social skills into manageable components and using positive reinforcement techniques, ABA therapy aims to empower individuals with autism to navigate social situations confidently. In this blog, we delve into the intricacies of ABA therapy and its impact on social dynamics within the autism community.
Understanding Social Challenges in Autism
Navigating social landscapes can feel like deciphering an intricate puzzle for individuals on the autism spectrum. The hallmark of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often involves difficulties in understanding social cues, interpreting emotions, and engaging in reciprocal communication. These challenges can lead to feelings of isolation and frustration, impacting various aspects of daily life, from forming friendships to succeeding in academic or professional environments. Moreover, the nuanced nature of social interactions can overwhelm individuals with autism, making it crucial to recognize and address these obstacles with targeted interventions such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. By delving into the unique social dynamics experienced by individuals with ASD, we gain valuable insights into the complexities they face and the importance of tailored support strategies.
The Role of ABA Therapy in Addressing Social Skills
ABA therapy emerges as a beacon of hope in the realm of autism intervention, offering structured techniques to enhance social skills and foster meaningful connections. At its core, ABA therapy operates on the principle of identifying specific behaviors, breaking them down into manageable components, and systematically reinforcing desired outcomes. When applied to social skills development, this approach empowers individuals with autism to grasp fundamental social concepts, such as turn-taking, nonverbal communication, and perspective-taking. By providing a structured framework for learning and practice, ABA therapy equips individuals with the tools they need to navigate social interactions confidently. Through consistent guidance and positive reinforcement, ABA therapists help bridge the gap between social challenges and meaningful social engagement for individuals with autism.
Breaking Down Social Interactions: ABA Approach
Breaking down social interactions is fundamental in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). ABA therapists systematically dissect complexities, making interactions more understandable. Through structured learning and guided support, individuals develop essential social skills gradually, fostering meaningful connections.
- Identifying specific social skills: ABA therapy targets skills such as initiating conversations, maintaining eye contact, and interpreting facial expressions.
- Structured learning opportunities: ABA therapists create structured exercises and role-playing scenarios to practice social skills in a controlled setting.
- Incremental progress: Individuals with ASD learn social skills step-by-step, gradually building confidence and competence over time.
- Repetition and reinforcement: Consistent practice and positive reinforcement help solidify social skills and improve retention.
- Guided feedback: ABA therapists provide constructive feedback and support to help individuals understand and improve their social interactions.
The ABA approach to breaking down social interactions offers a systematic and effective way for individuals with ASD to develop essential social skills. Through structured learning, incremental progress, and guided support, ABA therapy empowers individuals to navigate social situations with confidence and success.
Targeting Specific Social Skills Through ABA Techniques
Within the vast spectrum of social skills, individuals with autism may encounter challenges ranging from basic greetings to interpreting complex social cues. ABA therapy employs a repertoire of evidence-based techniques to target these specific skill deficits, fostering gradual progress and mastery. Task analysis, for instance, involves breaking down a complex social behavior into smaller, more manageable steps, facilitating systematic learning and practice. Role-playing and social scripts provide structured opportunities for individuals to rehearse social interactions in a controlled setting, honing their abilities through repetition and reinforcement. By tailoring interventions to address the unique needs of each individual, ABA therapy effectively targets specific social skills, laying the groundwork for improved social functioning and enhanced quality of life.
Individualized Strategies: Tailoring ABA for Social Success
In the realm of autism intervention, recognizing the unique needs of each individual is paramount. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy offers a tailored approach to address these needs and maximize social success. By conducting thorough assessments and identifying individual strengths, challenges, and preferences, ABA therapists craft personalized strategies to enhance social skills. These strategies are designed to be meaningful, relevant, and engaging, fostering motivation and participation in therapy. Through collaborative goal-setting and ongoing adjustments, individuals with autism receive the support they need to thrive socially.
- Comprehensive Assessments: ABA therapists conduct in-depth evaluations to understand each individual’s social strengths and challenges.
- Identification of Preferences: By recognizing personal interests and preferences, ABA therapists tailor interventions to align with the individual’s motivations.
- Goal-Setting Collaboration: Individuals and their families work together with ABA therapists to establish meaningful social goals.
- Flexible Intervention Approaches: ABA therapists adapt their techniques to accommodate sensory sensitivities and learning styles.
- Ongoing Adjustments: Continuous monitoring and adjustments ensure that interventions remain effective and relevant to the individual’s progress and needs.
Individualized strategies in ABA therapy empower individuals with autism to thrive socially by catering to their unique strengths and preferences. Through collaboration, flexibility, and ongoing adjustments, ABA therapists provide targeted support that fosters social growth and fulfillment.
Real-life Applications: ABA Therapy in Social Settings
While mastering social skills within the confines of a therapy session is essential, the ultimate goal of ABA therapy is to facilitate meaningful participation in real-life social settings. ABA therapists work collaboratively with individuals, families, and communities to generalize skills learned in therapy to various contexts, such as school, work, or leisure activities. By incorporating community outings, social clubs, and peer interactions into therapy sessions, ABA therapists bridge the gap between the clinical setting and the real world. Through guided support and gradual exposure, individuals with autism learn to apply their social skills in diverse environments, fostering independence and social integration.
Measuring Progress: Assessing Social Growth in ABA Therapy
Assessing social growth in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is crucial for tracking progress and tailoring interventions to individual needs. Through systematic data collection and analysis, therapists evaluate the effectiveness of social skills interventions, identifying areas of improvement and guiding further development. Using various assessment tools and techniques, ABA therapists gain valuable insights into the individual’s social competence and functioning over time.
- Data Collection: ABA therapists collect data on social behaviors and interactions during therapy sessions.
- Behavioral Observations: Therapists observe social behaviors in different contexts to assess generalization.
- Caregiver Reports: Input from caregivers provides valuable perspectives on social progress outside of therapy.
- Social Skills Assessments: Formal assessments measure specific social skills and track changes over time.
- Goal Setting: Setting measurable social goals helps guide therapy and monitor progress effectively.
Measuring progress in ABA therapy ensures that interventions are responsive to the evolving needs of individuals with autism, guiding them towards greater social competence and fulfillment. Through collaborative efforts and data-driven approaches, ABA therapists empower individuals to achieve meaningful social growth and integration.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing the social challenges faced by individuals with autism are paramount in facilitating their integration and success in society. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy stands as a powerful tool in this endeavor, offering structured approaches to enhance social skills and foster meaningful connections. By breaking down social interactions, targeting specific skills, and employing individualized strategies, ABA therapy equips individuals with autism with the tools they need to navigate social settings confidently. Real-life applications and progress monitoring ensure that interventions are effective and tailored to each individual’s needs. For those seeking support in Beavercreek, Ohio, Positive Solutions Behavior Group LLC offers comprehensive ABA therapy services at Contact us today to embark on a journey towards social growth and fulfillment.